Male Pattern Baldness: What are the Different Stages of Hair Loss in Men?
Evidence Based
All the information in this blog post is accurate, trustworthy, scientifically based and has been written and fact-checked by our experts and doctors.
Our licensed nutritionists and dietitians are committed to being objective, unbiased and honest, presenting all sides of the argument.
This article includes scientific references in brackets, which are clickable links to research papers from reputable academic organizations.

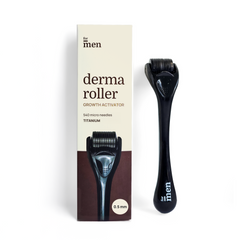
Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common type of hair loss in men. It affects over half of men over the age of 50 and usually begins in the late teens or early twenties.
Male Pattern Baldness Symptoms and Progression:
- The hairline typically recedes at the temples, forming an "M" shape.
- Thinning hair occurs on the crown of the head, progressing to a bald patch or horseshoe-shaped pattern.
- Hair loss usually continues gradually over time, although the rate can vary greatly.
Male Pattern Baldness Causes:
- Genetics: Male pattern baldness is strongly linked to family history. If your father or grandfather had it, you're more likely to experience it too.
- Hormones: Androgens, specifically dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a key role in hair loss. DHT shrinks hair follicles over time, leading to shorter and finer hair, eventually stopping hair growth altogether.
- Other Factors: Age, stress, diet, and certain medical conditions can also contribute to hair loss, although their role is less understood than genetics and hormones.
Male Pattern Baldness Treatment Options:
Medications:
Minoxidil and finasteride are FDA-approved medications that can slow down hair loss and even promote some hair regrowth. They work by either increasing blood flow to hair follicles (minoxidil) or blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT (finasteride).
Hair Transplantation:
Hair Transplantation surgical procedure involves transplanting hair follicles from the back of the scalp (where they are less affected by DHT) to the balding areas.
Laser Therapy:
Low-level laser therapy may stimulate hair growth in some individuals, but the evidence is limited and it's not considered a first-line treatment.
Hairpieces and Wigs:
These can provide a cosmetic solution for those who don't want or can't undergo other treatments.
Staging Male Pattern Baldness:
While there isn't a single universally accepted scale to stage baldness, there are three widely used systems for classifying the progression of male pattern hair loss:
1. The Norwood-Hamilton Scale:
This is the most popular and widely used system, with seven stages defined by the extent of hair loss at the temples, crown, and overall density. However, some criticize it for being too detailed and not encompassing all possible patterns.
2. The Ludwig Scale:
This scale focuses on female pattern hair loss, with three main types and subcategories within each. It's helpful for understanding different patterns of thinning in women.
3. The Savin Scale:
This system uses six stages based on the degree of scalp visibility through the hair. It's simpler than the Norwood-Hamilton scale but lacks specific details about hairline recession or crown thinning.
The Norwood-Hamilton Scale in Detail:
Following are the different stages of the Norwood-Hamilton Scale.
- Stage 1: This stage represents minimal hair loss, with a mature hairline with slight recession at the temples.
- Stage 2: This stage shows further recession at the temples, forming an M-shape hairline.
- Stage 3: In this stage, the receding hairline progresses further, and thinning occurs on the vertex (crown) of the scalp.
- Stage 4: This stage features a more pronounced bald area on the crown, with the remaining hair forming a bridge between the temples.
- Stage 5: At this stage, the bald area on the crown expands significantly, and the bridge of hair becomes narrower.
- Stage 6: This stage shows a horseshoe-shaped pattern of remaining hair at the front and sides of the head, with a large bald area on the crown.
- Stage 7: This stage represents the most advanced hair loss, with only a thin rim of hair remaining around the back and sides of the head.
Important Points to Consider:
- The Norwood-Hamilton scale primarily focuses on male pattern hair loss, but it can also be adapted to female pattern hair loss to some extent.
- The rate of progression through the stages can vary significantly among individuals.
- The scale doesn't account for all possible hair loss patterns.
- Focusing solely on the stage can be emotionally sensitive and may not capture the whole picture of hair health.
Important Points:
- Early diagnosis and treatment can be helpful in slowing down hair loss and potentially promoting some regrowth.
- There is no cure for male pattern baldness, but there are effective treatments available.
- Talk to your doctor to discuss the best treatment options for you based on your individual needs and preferences.
- Remember, hair loss is a common experience, and it's important to focus on overall health and well-being rather than just the cosmetic aspect.
We should be on our hair and scalp health right from our 20’s itself so as to have a head full of hair in our 50’s!
Also Read the Articles:
Disclaimer: The information provided on this page is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any questions or concerns about your health, please talk to a healthcare professional.
 Evidence Based
Evidence Based



Leave a comment